Bitcoin currency vs. Economy 101: Powerful Insights and Future Outlook 2025
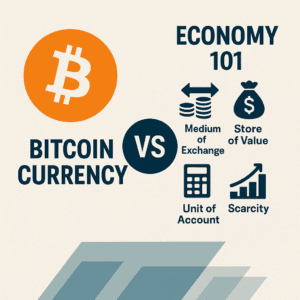
At its core, Bitcoin currency represents a radical shift in how we define and use money. Traditional economics teaches us that money plays three essential roles—medium of exchange, store of value, and unit of account—and must possess characteristics like durability, stability, scarcity, portable, and acceptance to perform well. So where does Bitcoin fit into that model? In this article, we unpack the evolution of money from Econ 101 basics to digital alternatives, assess Bitcoin’s performance on those timeless metrics, and analyze how Bitcoin currency interacts with traditional economies in 2025 and beyond.
For further insight into its market performance, see this expert analysis on Bitcoin’s future and price prediction 2025.
Section 1: The Fundamentals of Money – Econ 101 Framework
In every introductory macroeconomics course, money is defined by its three primary functions:
Medium of Exchange: Money enables efficient trading by eliminating barter.
Store of Value: Money preserves purchasing power.
Unit of Account: Money provides a consistent measure for valuing goods and services.
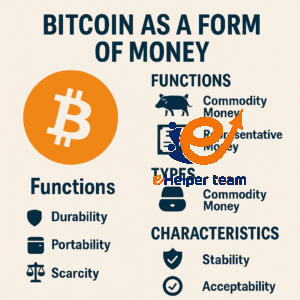
Equally important are the types of money: commodity money, representative money, and fiat money. Bitcoin currency doesn’t neatly fit into these traditional categories, hinting at a new financial paradigm.
For a broader understanding of crypto as a new category of money, E Helper Team’s cryptocurrency guide offers essential reading.
Section 2: Bitcoin Currency Evaluated Against Econ 101 Principles
Medium of Exchange
Bitcoin can be used for purchases, but global merchant acceptance is limited. Services that convert Bitcoin to fiat at the point of sale are helping bridge this gap.
Store of Value
Bitcoin’s volatility is its Achilles’ heel. Its swings prevent it from being considered a fully reliable store of value.
Unit of Account
It is not widely used for pricing goods, though in crypto ecosystems, Bitcoin acts as a benchmark currency.
For an innovative real-world example, see how projects like Satoshi Island are experimenting with blockchain-driven communities where cryptocurrencies might function as the main unit of account.
Section 3: Scoring Bitcoin—A 30-Point Econ 101 Style Analysis
Using a scoring framework:
Functions: 6/10
Characteristics: 8/10
Types: 4/10
Overall score: 18/30 (60%). This shows Bitcoin has potential but lacks stability and acceptance.
Section 4: Macroeconomic Implications of Bitcoin Currency
Bitcoin introduces possibilities for cross-border trade efficiency and an alternative to inflation-prone fiat currencies. However, governments remain cautious, with regulation increasing worldwide.
For investors considering automation and AI-driven portfolios, platforms like those reviewed in this comprehensive guide to automated crypto investing can be useful in navigating Bitcoin’s macroeconomic role.
Section 5: Challenges and Future Outlook
Bitcoin faces hurdles:
Volatility: discourages mass adoption.
Regulation: governments aim to control or restrict usage.
Competition: stablecoins and CBDCs are evolving fast.
But as long as demand for decentralized money exists, Bitcoin will remain at the forefront.
Section 6: Practical Uses and Earning with Bitcoin Currency
You can earn Bitcoin through mining, trading, and long-term holding. Mining, though less profitable for individuals today, remains a key method.
For secure options, see this list of top 5 credible cloud mining sites for Bitcoin.
Investors should diversify, use reliable wallets, and stay updated on regulations to minimize risks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What exactly is “Bitcoin currency”?
Bitcoin currency is a decentralized digital form of money that operates on blockchain technology. Unlike traditional fiat currencies issued by governments, Bitcoin is created through a process called mining and is maintained by a global network of computers. It allows peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries like banks, making it unique in the financial world.
2. Can Bitcoin currency truly function like money according to Econ 101 principles?
According to economic theory, money must serve as a medium of exchange, a store of value, and a unit of account. Bitcoin partially fulfills these roles—it is highly portable, divisible, and scarce, but its volatility and limited global acceptance prevent it from fully replacing traditional fiat money at this stage.
3. Why is Bitcoin so volatile compared to traditional currencies?
Bitcoin’s price fluctuates heavily due to several factors:
Speculative trading by retail and institutional investors.
Limited supply capped at 21 million coins.
Market sentiment influenced by news, regulations, or economic uncertainty.
Low liquidity compared to global fiat markets.
This volatility makes it attractive for traders but risky as a stable currency.
4. How does Bitcoin currency compare to fiat money like the US Dollar or Euro?
Fiat money is government-backed, widely accepted, and stable in daily use. Bitcoin, on the other hand, is decentralized, limited in supply, and not tied to any government. While fiat is better for stable transactions, Bitcoin is often seen as “digital gold” for investors seeking long-term value or protection against inflation.
5. What are the main risks of using Bitcoin currency?
Volatility: Prices can swing dramatically within hours.
Regulatory uncertainty: Some governments ban or restrict Bitcoin use.
Cybersecurity threats: Hacks and scams in exchanges and wallets are common.
Limited acceptance: Not all merchants or financial systems integrate Bitcoin.
Irreversible transactions: Once sent, a Bitcoin payment cannot be undone.
6. Will Bitcoin ever become a mainstream medium of exchange?
Possibly, but it depends on key factors:
Stability: Bitcoin needs reduced volatility to function like fiat.
Merchant adoption: Wider acceptance by global retailers and payment platforms.
Government stance: Regulatory clarity and cooperation with financial systems.
Technological scaling: Solutions like the Lightning Network aim to make transactions faster and cheaper, potentially boosting adoption.
7. How can someone earn or invest in Bitcoin currency safely?
There are several ways:
Buying and holding (HODLing) through reputable exchanges.
Trading based on price swings.
Mining or cloud mining (though costly for individuals).
Staking through platforms that support Bitcoin derivatives.
For safe investing, use trusted exchanges, enable two-factor authentication, and never invest more than you can afford to lose.
8. Is Bitcoin currency an inflation hedge like gold?
Many investors view Bitcoin as a hedge since its supply is capped at 21 million. However, unlike gold, Bitcoin lacks centuries of historical stability. While it may protect against inflation in some cases, its volatility means it cannot yet fully replace gold as a safe haven.
Conclusion
Bitcoin currency currently meets 60% of Econ 101 criteria. Its strengths lie in portability and scarcity, but instability and limited adoption slow its evolution. Despite challenges, it continues shaping global discussions on the future of money.





